What Is Agarwood And Agarwood Oil? A Complete Guide!
Agarwood, also known as Oud, is a highly prized resinous wood that forms in the heartwood of Aquilaria trees when they become infected with a type of mold. This rare and precious wood has been used for centuries in perfumery, incense, and traditional medicine across various cultures.
Agarwood Oil, extracted from this wood, is renowned for its rich, complex aroma and is considered one of the most expensive essential oils in the world.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore the fascinating world of Agarwood and Agarwood Oil, delving into their history, production, uses, benefits, and more.
What Is Agarwood?
Agarwood, scientifically known as Aquilaria, is a dark, resinous heartwood that forms in trees of the Aquilaria and Gyrinops genera, native to Southeast Asia, including countries like India, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Vietnam.

The formation of Agarwood is a result of the tree’s defense mechanism against infection by the mold Phaeoacremonium parasitica, often initiated by damage from Ambrosia beetles. The infected tree produces a fragrant resin that accumulates in the heartwood, creating the valuable Agarwood.
Not all Aquilaria trees produce Agarwood; only about 7% do so naturally. Due to its rarity and the time-consuming process of formation, Agarwood is one of the most expensive woods in the world, with prices for high-quality specimens reaching up to $100,000 per kilogram.
History of Agarwood
The use of Agarwood dates back thousands of years. Historical records indicate that as early as the third century CE, Agarwood was collected in what is now Central Vietnam, as mentioned in the Chinese chronicle Nan zhou yi wu zhi.
In Japan, the Nihon Shoki, a historical text from the sixth century CE, records the discovery of a large piece of Agarwood from Cambodia, which is still preserved and occasionally displayed at the Nara National Museum.
Agarwood holds significant cultural and religious importance in various traditions. In Hinduism, it is associated with Lord Krishna, and in Buddhism, it is considered the “scent of Nirvana.” Islamic scriptures also mention Agarwood, and it has been used in Chinese folk religion. Samurai warriors in Japan perfumed their armor with Agarwood smoke for good luck before battles.
During the Renaissance, Agarwood was a prized possession in European courts, with Grand Duke Ferdinando II de Medici purchasing a large piece for a substantial sum, highlighting its value and rarity.
How Is Agarwood Formed?
Agarwood formation is a natural process that occurs when Aquilaria trees are infected by the mold Phaeoacremonium parasitica. This infection often follows physical damage to the tree, such as from Ambrosia beetles or natural events like storms. In response, the tree produces a resin to protect itself, which over time accumulates in the heartwood, transforming it into Agarwood.
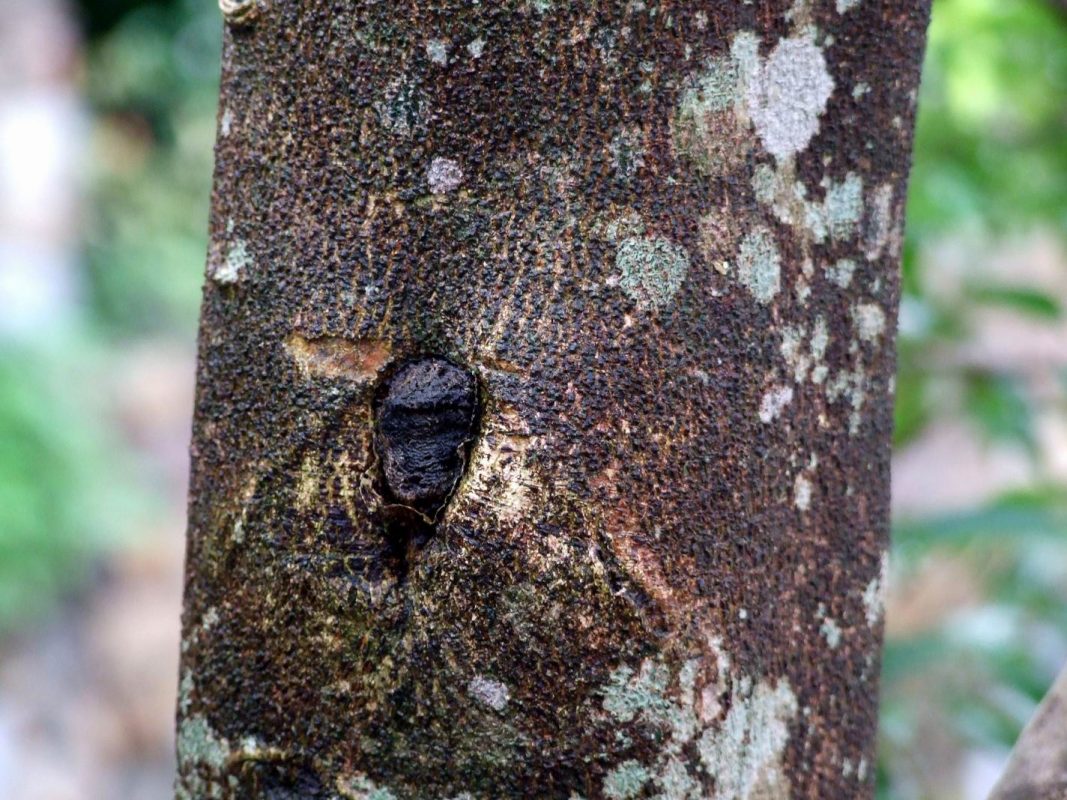

The process can take several years, and the quality of the wood depends on factors such as the species of the tree, the duration of infection, and environmental conditions. In natural settings, only a small fraction of Aquilaria trees develop Agarwood, making it extremely rare.
To meet the high demand, artificial induction methods have been developed, including physical wounding, chemical inducers, and inoculation with fungi. While artificially induced Agarwood can be produced more reliably, it may not always match the quality of naturally formed Agarwood.
Types Of Agarwood
Agarwood is produced by several species of Aquilaria and Gyrinops trees, with Aquilaria malaccensis, A. crassna, and A. sinensis being the most prominent. Each species produces Agarwood with slightly different characteristics in terms of aroma and resin content.
Agarwood is also classified based on its quality, which is influenced by the amount of resin, the age of the tree, and the region where it was harvested. Different countries have their own grading systems:
| Country | Grading System |
| Malaysia | Double Super, Super, A, B, C, D |
| Indonesia | Super A, Super B, Super C, Sabak |
| India | Triple Super, Double Super, Super, A, B, C, D |
| Bangladesh | Triple Super, Double Super, Super, A, B, C, D |
| Vietnam | Grade 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 (1 is highest) |
The highest grades are reserved for Agarwood with the darkest color and highest resin content, which typically have the most intense and complex aromas.
What Is Agarwood Oil?
Agarwood Oil, commonly known as Oud Oil, is an essential oil extracted from the resinous heartwood of Agarwood. It is obtained through steam or hydro distillation, where the wood is processed to release the oil. The resulting oil is thick, dark brown, and has a rich, woody aroma with notes of earthiness, smokiness, and sometimes sweetness.

Due to the labor-intensive extraction process and the scarcity of high-quality Agarwood, Oud Oil is one of the most expensive essential oils, with prices that can exceed $50,000 per liter.
Extraction Methods of Agarwood Oil
The primary method for extracting Agarwood Oil is steam distillation, where steam is passed through Agarwood chips, vaporizing the essential oil, which is then condensed and collected. Another method is hydro distillation, where the wood is boiled in water, and the oil is separated from the water.
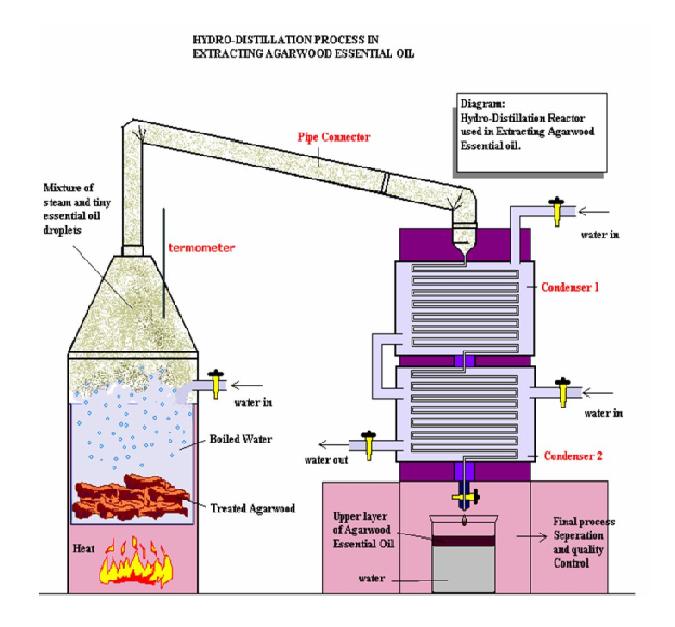
The quality of the oil depends on the quality of the Agarwood used and the distillation technique. Traditional methods may involve longer distillation times to capture the full spectrum of aromatic compounds, while modern methods might use more efficient equipment to maximize yield.
Uses of Agarwood
Agarwood, often referred to as “liquid gold” due to its rarity and value, has been treasured for centuries across various cultures. Its unique fragrance and spiritual significance make it highly sought-after in many industries. Here are the primary uses of Agarwood:
1. Incense
Agarwood chips and powder are commonly burned as incense, releasing a rich, complex aroma. This smoke is deeply associated with spirituality and is used in:
- Religious Ceremonies: In Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islamic traditions, Agarwood incense is burned to purify the air and create a sacred atmosphere for prayer and rituals.
- Meditation and Yoga: The calming scent enhances focus and tranquility, helping practitioners enter a deeper meditative state.
- Aromatherapy: Agarwood is believed to relieve stress, anxiety, and insomnia, making it a popular choice for therapeutic use in homes and spas.
2. Perfumery
Agarwood oil, also known as Oud oil, is one of the most prized ingredients in high-end perfumery. It is used as a base note in luxury fragrances due to its long-lasting, musky, and woody aroma. Notable points include:
- Blending Qualities: Its rich, complex scent profile blends well with floral, spicy, and citrus top notes, adding depth and sensuality.
- Symbol of Prestige: Oud-based perfumes are often seen as a mark of status and sophistication, especially in the Middle East and Europe.
- Natural Fixative: Agarwood oil helps stabilize other perfume components, ensuring the scent lasts longer on the skin.
3. Traditional Medicine
In traditional medicinal systems such as Ayurveda, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), and Unani, Agarwood has been used for centuries for its therapeutic properties:
- Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic: It is believed to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, especially in conditions like arthritis or muscle aches.
- Digestive Aid: Agarwood powder or oil is sometimes used to treat indigestion, nausea, and bloating.
- Mental Health: Traditionally, it is used to calm the mind, reduce anxiety, and treat conditions like epilepsy or hysteria.
- Respiratory Support: Agarwood is used in some cultures to treat asthma, coughs, and bronchial problems.
4. Carvings and Artifacts
High-grade Agarwood is also used to create handcrafted items that are both beautiful and aromatic:
- Religious and Spiritual Objects: Items like mala beads, rosaries, and amulets are made from Agarwood, prized for their spiritual energy and fragrant properties.
- Decorative Art: Sculptures, fans, and intricate carvings made from Agarwood are valued as luxury items or collectibles.
- Cultural Gifts: In some countries, gifting Agarwood carvings is seen as a gesture of deep respect and honor.
Uses Of Agarwood Oil
Extracted from the heartwood of Aquilaria trees infected by a specific type of mold, this rare and aromatic oil has a wide range of uses across different industries and traditions. Below are the key areas where Agarwood oil plays a significant role:
1. Perfumery
Agarwood oil is a cornerstone of luxury perfumery, especially in the Middle East, Europe, and parts of Asia.
- Signature Scent: Its deep, woody, musky, and slightly sweet fragrance creates a distinctive base note that lingers on the skin for hours.
- Blending Power: Oud oil harmonizes well with floral, amber, and spice accords, allowing perfumers to craft complex and long-lasting fragrances.
- Symbol of Opulence: Perfumes containing Oud are often marketed as premium products, associated with royalty, elegance, and exclusivity.
- Natural Fixative: The oil stabilizes other volatile ingredients in perfume blends, enhancing both performance and shelf life.
2. Aromatherapy
Agarwood oil has long been cherished in holistic wellness practices for its emotional and spiritual benefits.
- Stress Relief: The warm and grounding scent of Agarwood oil helps reduce anxiety, tension, and emotional fatigue.
- Meditation and Spiritual Practice: Used in diffusers or applied to pulse points, it deepens concentration and creates a serene ambiance, ideal for yoga and meditation.
- Mood Enhancement: Many users report improved clarity, focus, and emotional balance when using Agarwood oil in aromatherapy.
3. Skincare
A growing number of natural and luxury skincare brands are incorporating Agarwood oil into their formulations.
- Anti-aging Properties: Rich in antioxidants, it helps combat free radicals, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Moisturizing Effect: Its emollient nature helps to hydrate and nourish dry or sensitive skin.
- Soothing Benefits: It may reduce inflammation and irritation, making it suitable for calming troubled skin or conditions like eczema.
- Natural Fragrance: Agarwood oil imparts a gentle, exotic aroma to skincare products without the need for synthetic perfumes.
4. Medicinal Applications
In traditional medicine systems such as Ayurveda, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), and Unani, Agarwood oil is used to treat a wide range of health issues.
- Digestive Support: Historically used as a remedy for indigestion, bloating, and abdominal discomfort.
- Respiratory Relief: Inhaling its vapors or using it in balms may help ease coughs, asthma, and bronchial congestion.
- Skin Conditions: Applied topically in diluted form, it may help treat rashes, wounds, and fungal infections due to its potential anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
- Pain Management: Used in massage oils, it may relieve muscle aches, joint pain, and headaches.
Benefits of Agarwood and Agarwood Oil
Agarwood and its essential oil have been valued for centuries in spiritual, medicinal, and cosmetic traditions across Asia and the Middle East. Modern science is beginning to explore and support some of these ancient beliefs. Below is a comprehensive look at their potential benefits:
Benefits of Agarwood
Below Are the benefits of Agarwood:
1. Spiritual Significance
Agarwood has deep-rooted spiritual and cultural importance in many religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, and Christianity.
- Purification Rituals: Burning Agarwood chips or powder is believed to cleanse the environment of negative energy and spiritual impurities.
- Enhancing Meditation: The rich, calming scent is used to deepen focus during prayer, meditation, and other spiritual practices.
- Symbol of Reverence: In temples and homes, Agarwood is often offered to deities or burned during sacred ceremonies, signifying respect and devotion.
2. Aromatherapy and Emotional Balance
The scent of Agarwood is known for its grounding, warming, and tranquil effects on the mind and body.
- Reduces Anxiety and Tension: Inhaling the smoke or using Agarwood incense can create a serene atmosphere, relieving mental clutter and promoting calm.
- Improves Sleep Quality: The calming properties of its aroma may help induce sleep, especially when used before bedtime in aromatherapy routines.
- Promotes Emotional Stability: It is thought to balance emotional highs and lows, making it a natural aid for managing mood swings.
Benefits of Agarwood Oil (Oud Oil)
Below Are the benefits of Agarwood Oil:
1. Anti-inflammatory Properties
Preliminary scientific studies and traditional usage suggest that Agarwood oil may help reduce inflammation.
- Joint and Muscle Relief: When used in massage oils or balms, it may ease symptoms of arthritis, sore muscles, and other inflammatory conditions.
- Skin Soothing: Its anti-inflammatory action may help calm irritated skin, rashes, or allergic reactions.
2. Antimicrobial Effects
Agarwood oil has demonstrated antibacterial and antifungal properties in lab studies.
- Wound Healing: It may aid in the prevention of infections when applied to minor cuts or abrasions (always diluted).
- Fungal Infections: It can potentially combat fungal issues like athlete’s foot or candidiasis, supporting skin and scalp health.
- Natural Preservative: Due to its antimicrobial nature, it may also be used in natural cosmetic formulations as a mild preservative.
3. Mental Health and Emotional Wellness
The psychological benefits of Agarwood oil are one of its most celebrated attributes.
- Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Effects: The complex aroma is believed to stimulate the limbic system, which governs emotions—helping to uplift mood and reduce feelings of anxiety or sadness.
- Stress Reduction: Used in diffusers or aromatherapy massages, it can promote emotional balance and resilience in stressful environments.
- Mental Clarity: Some users report enhanced focus and concentration, making it suitable for study, creative work, or meditation.
4. Skin Health and Beauty
Agarwood oil is increasingly being used in natural and luxury skincare due to its rejuvenating properties.
- Promotes Skin Regeneration: The oil may support the renewal of skin cells, contributing to a brighter, more youthful complexion.
- Anti-aging Effects: Rich in antioxidants, it may reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
- Scar Reduction: Traditionally, it’s been used to reduce the visibility of scars and blemishes, especially in healing blends with other carrier oils.
Scientific and Traditional Support
While many of these benefits are supported by centuries of traditional use in Ayurvedic, Chinese, and Middle Eastern medicine, modern scientific research is still in the early stages. Preliminary studies—such as those published on PubMed Central (PMC)—highlight promising anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and mood-enhancing properties, but further clinical trials are needed for full medical validation.
Agarwood in Different Cultures
Agarwood, often referred to as “wood of the gods,” holds deep cultural, religious, and medicinal importance across many regions of the world. Its exquisite fragrance and symbolic power have made it a revered substance for centuries. Below is a deeper look into how different cultures use and honor Agarwood:
Middle East
- Known as “Oud,” Agarwood is one of the most treasured materials in Arab culture.
- Perfumery Legacy: Oud oil is considered the heart of traditional Arabic perfumery. It is blended into rich, complex fragrances that are worn daily and on special occasions.
- Social Symbol: The use of Oud is a sign of hospitality and wealth. In many homes and gatherings, Agarwood is burned to welcome guests, create a luxurious atmosphere, and express refinement.
- Religious Use: Oud incense is commonly used in mosques and during religious events, particularly during Ramadan and Eid, to purify the environment and uplift the spirit.
Japan
- Kōdō (“The Way of Incense”): In Japan, Agarwood is central to Kōdō, an ancient and refined incense ceremony that dates back to the Heian period (794–1185).
- Spiritual and Artistic Appreciation: Unlike casual incense burning, Kōdō is a meditative and ritualistic experience where participants “listen” to the fragrance of different types of Agarwood in a formal setting.
- Cultural Artifacts: High-quality Agarwood, especially Kyara, is extremely rare and often preserved as a national treasure or heirloom.
China
- Traditional Medicine: In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Agarwood is believed to balance “Qi” (vital energy) and is used to treat digestive disorders, anxiety, and respiratory issues.
- Cultural Heritage: During festivals or temple ceremonies, Agarwood incense is burned as an offering to ancestors and deities, symbolizing reverence, purity, and connection with the divine.
- Luxury and Status: Agarwood carvings, incense holders, and oil are considered symbols of elegance and often gifted among the elite.
India
- Spiritual Essence: Agarwood is deeply associated with Hindu spiritual practices, especially during prayer, meditation, and purification rituals.
- Ayurvedic Use: In Ayurveda, it is used to treat a wide range of ailments, including mental disorders, inflammation, and skin diseases. It is valued for its warming and grounding properties.
- Cultural Symbolism: Agarwood is believed to attract positive energy and dispel negativity, making it a preferred choice for religious altars and spiritual sanctuaries.
Bangladesh
- Spiritual Practice: In Bangladesh, Agarwood is linked to Islamic traditions and Sufi rituals, where the scent is believed to promote a deeper spiritual connection.
- Ayurvedic and Folk Medicine: Like in India, Agarwood is used in herbal formulations for its calming, digestive, and therapeutic benefits.
- Economic and Cultural Role: As one of the countries where Agarwood cultivation is expanding, it holds growing importance in both cultural heritage and local livelihoods.
A Universal Treasure
Each culture has developed its own unique customs and rituals around Agarwood, from formal incense ceremonies in Japan to spiritual offerings in South Asia and luxurious perfumery in the Middle East. Despite these cultural differences, one common thread unites them all: a deep reverence for the rare and sacred nature of Agarwood.
Agarwood in Perfumery
In perfumery, Agarwood is revered for its complex and long-lasting scent. It is often used as a base note, providing depth and richness to fragrances. The aroma can vary widely, from sweet and floral to deep and animalic, depending on the source and quality. Many luxury perfume brands incorporate Agarwood Oil, and its uniqueness adds to the exclusivity of these fragrances.
Agarwood in Medicine
Traditionally, Agarwood has been used in various medicinal systems:
- Ayurveda: Used to treat digestive disorders, respiratory issues, and as a general tonic.
- Traditional Chinese Medicine: Believed to promote circulation, relieve pain, and calm the mind.
Modern research has begun to validate some of these uses, demonstrating anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antimicrobial properties. However, these findings are preliminary, and more research is needed to establish safe and effective uses in modern medicine.
Sustainability and Conservation of Agarwood
Due to overharvesting and illegal logging, many Aquilaria species are now endangered. Efforts are being made to cultivate Agarwood sustainably through plantations where trees are artificially induced to produce resin. Consumers can support conservation by purchasing from suppliers who practice sustainable harvesting and provide certification of origin.
International regulations, such as those enforced by CITES, aim to control the trade of Agarwood to prevent further depletion of wild populations.
How to Identify Genuine Agarwood and Agarwood Oil
Due to its high value, Agarwood and its oil are often subject to adulteration. Here are tips to identify genuine products:
For Agarwood
- Visual Inspection: Look for natural color variations and oil veins. Genuine Agarwood has a rich, dark color with visible resin lines OUD Vietnam: How to Identify Real Agarwood Bracelet.
- Scent: Real Agarwood has a subtle, complex aroma. When burned, it produces a pleasant fragrance with minimal smoke.
- Density: High-quality Agarwood is dense and may sink in water.
For Agarwood Oil
- Source: Purchase from reputable suppliers who provide information on origin and extraction method.
- Aroma: Genuine Agarwood Oil has a deep, woody scent that evolves over time, not synthetic or overly sweet.
- Consistency: It is typically thick and dark brown.
- Price: Be wary of prices that seem too low, as high-quality Agarwood Oil is expensive.
Scientific methods like gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) can be used for precise verification.
Agarwood and Agarwood Oil are treasures of nature, offering a unique combination of aromatic beauty and potential health benefits. From their ancient historical roots to their modern-day applications in perfumery and medicine, these products continue to captivate and inspire.
As we appreciate their value, it is crucial to support sustainable practices to ensure that future generations can also experience the wonders of Agarwood.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Agarwood?
Agarwood is a resinous heartwood from Aquilaria trees, formed when the tree is infected by a mold, producing a fragrant resin.
- How is Agarwood formed?
It forms naturally when Aquilaria trees are infected by Phaeoacremonium parasitica mold, often after damage by insects or natural events.
- What is Agarwood Oil used for?
It is used in perfumery, aromatherapy, skincare, and traditional medicine.
- How is Agarwood Oil extracted?
Through steam or hydro distillation of the resinous heartwood.
- What are the benefits of Agarwood Oil?
It has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and potential mental health benefits, among others.
- Is Agarwood endangered?
Yes, many Aquilaria species are endangered due to overharvesting.
- How can I tell if Agarwood is genuine?
Look for natural color variations, oil veins, and a subtle, complex aroma. For oil, ensure it comes from a reputable source.
- What does Agarwood smell like?
It has a woody, earthy, slightly smoky aroma with complex notes that can include sweetness or floral hints.
- How much does Agarwood cost?
Prices vary widely, from hundreds to thousands of dollars per kilogram for wood, and up to $1,00,000 per liter for high-quality oil.
- Where can I buy Agarwood or Agarwood Oil?
Purchase from reputable suppliers who provide certification of origin and practice sustainable harvesting.






